Definition
The absolute value (or modulus) of a real number x is x's numerical value without regard to its sign.
of a real number x is x's numerical value without regard to its sign.
For example, ;
;  ;
; 
Graph:
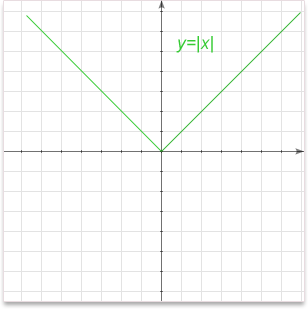
Important properties:





3-steps approach:
General approach to solving equalities and inequalities with absolute value:
1. Open modulus and set conditions.
To solve/open a modulus, you need to consider 2 situations to find all roots:
For example,
a) Positive: if , we can rewrite the equation as:
, we can rewrite the equation as: 
b) Negative: if , we can rewrite the equation as:
, we can rewrite the equation as: 
We can also think about conditions like graphics. is a key point in which the expression under modulus equals zero. All points right are the first conditions
is a key point in which the expression under modulus equals zero. All points right are the first conditions  and all points left are second conditions
and all points left are second conditions  .
.
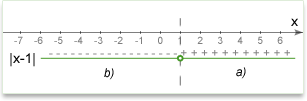
2. Solve new equations:
a) --> x=5
--> x=5
b) --> x=-3
--> x=-3
3. Check conditions for each solution:
a) has to satisfy initial condition
has to satisfy initial condition  .
.  . It satisfies. Otherwise, we would have to reject x=5.
. It satisfies. Otherwise, we would have to reject x=5.
b) has to satisfy initial condition
has to satisfy initial condition  .
.  . It satisfies. Otherwise, we would have to reject x=-3.
. It satisfies. Otherwise, we would have to reject x=-3.
3-steps approach for complex problems
Let’s consider following examples,
Example #1
Q.: . How many solutions does the equation have?
. How many solutions does the equation have?
Solution: There are 3 key points here: -8, -3, 4. So we have 4 conditions:
a) .
.  -->
-->  . We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-1 is not less than -8)
. We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-1 is not less than -8)
b) .
.  -->
-->  . We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-15 is not within (-8,-3) interval.)
. We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-15 is not within (-8,-3) interval.)
c) .
.  -->
-->  . We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-15 is not within (-3,4) interval.)
. We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-15 is not within (-3,4) interval.)
d) .
.  -->
-->  . We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-1 is not more than 4)
. We reject the solution because our condition is not satisfied (-1 is not more than 4)
(Optional) The following illustration may help you understand how to open modulus at different conditions.
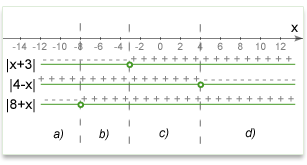
Answer: 0
Example #2
Q.: . What is x?
. What is x?
Solution: There are 2 conditions:
a) -->
-->  or
or  .
.  -->
-->  . x e {
. x e { ,
,  } and both solutions satisfy the condition.
} and both solutions satisfy the condition.
b) -->
-->  .
.  -->
-->  . x e {
. x e { ,
,  } and both solutions satisfy the condition.
} and both solutions satisfy the condition.
(Optional) The following illustration may help you understand how to open modulus at different conditions.
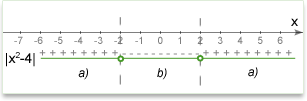
Answer: ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
Tip & Tricks
The 3-steps method works in almost all cases. At the same time, often there are shortcuts and tricks that allow you to solve absolute value problems in 10-20 sec.
I. Thinking of inequality with modulus as a segment at the number line.
For example,
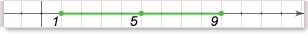
Problem: 1<x<9. What inequality represents this condition?
A. |x|<3
B. |x+5|<4
C. |x-1|<9
D. |-5+x|<4
E. |3+x|<5
Solution: 10sec. Traditional 3-steps method is too time-consume technique. First of all we find length (9-1)=8 and center (1+8/2=5) of the segment represented by 1<x<9. Now, let’s look at our options. Only B and D has 8/2=4 on the right side and D had left site 0 at x=5. Therefore, answer is D.
II. Converting inequalities with modulus into range expression.
In many cases, especially in DS problems, it helps avoid silly mistakes.
For example,
|x|<5 is equal to x e (-5,5).
|x+3|>3 is equal to x e (-inf,-6)&(0,+inf)
III. Thinking about absolute values as distance between points at the number line.
For example,
Problem: A<X<Y<B. Is |A-X| <|X-B|?
1) |Y-A|<|B-Y|
Solution:
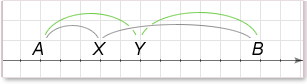
We can think about absolute values here as distance between points. Statement 1 means than distance between Y and A is less than Y and B. Because X is between A and Y, distance between |X-A| < |Y-A| and at the same time distance between X and B will be larger than that between Y and B (|B-Y|<|B-X|). Therefore, statement 1 is sufficient.
Pitfalls
The most typical pitfall is ignoring third step in opening modulus - always check whether your solution satisfies conditions.
Official GMAC Books:
The Official Guide, 12th Edition: PS #22; PS #50; PS #130; DS #1; DS #153;
The Official Guide, Quantitative 2th Edition: PS #152; PS #156; DS #96; DS #120;
The Official Guide, 11th Edition: DT #9; PS #20; PS #130; DS #3; DS #105; DS #128;
Generated from [GMAT ToolKit]
Resources
Absolute value DS problems: [search]
Absolute value PS problems: [search]
Fig's post with absolute value problems: [Absolute Value Problems]
For more information click here
The absolute value (or modulus)
For example,
Graph:
Important properties:
3-steps approach:
General approach to solving equalities and inequalities with absolute value:
1. Open modulus and set conditions.
To solve/open a modulus, you need to consider 2 situations to find all roots:
- Positive (or rather non-negative)
- Negative
For example,
a) Positive: if
b) Negative: if
We can also think about conditions like graphics.
2. Solve new equations:
a)
b)
3. Check conditions for each solution:
a)
b)
3-steps approach for complex problems
Let’s consider following examples,
Example #1
Q.:
Solution: There are 3 key points here: -8, -3, 4. So we have 4 conditions:
a)
b)
c)
d)
(Optional) The following illustration may help you understand how to open modulus at different conditions.
Answer: 0
Example #2
Q.:
Solution: There are 2 conditions:
a)
b)
(Optional) The following illustration may help you understand how to open modulus at different conditions.
Answer:
Tip & Tricks
The 3-steps method works in almost all cases. At the same time, often there are shortcuts and tricks that allow you to solve absolute value problems in 10-20 sec.
I. Thinking of inequality with modulus as a segment at the number line.
For example,
Problem: 1<x<9. What inequality represents this condition?
A. |x|<3
B. |x+5|<4
C. |x-1|<9
D. |-5+x|<4
E. |3+x|<5
Solution: 10sec. Traditional 3-steps method is too time-consume technique. First of all we find length (9-1)=8 and center (1+8/2=5) of the segment represented by 1<x<9. Now, let’s look at our options. Only B and D has 8/2=4 on the right side and D had left site 0 at x=5. Therefore, answer is D.
II. Converting inequalities with modulus into range expression.
In many cases, especially in DS problems, it helps avoid silly mistakes.
For example,
|x|<5 is equal to x e (-5,5).
|x+3|>3 is equal to x e (-inf,-6)&(0,+inf)
III. Thinking about absolute values as distance between points at the number line.
For example,
Problem: A<X<Y<B. Is |A-X| <|X-B|?
1) |Y-A|<|B-Y|
Solution:
We can think about absolute values here as distance between points. Statement 1 means than distance between Y and A is less than Y and B. Because X is between A and Y, distance between |X-A| < |Y-A| and at the same time distance between X and B will be larger than that between Y and B (|B-Y|<|B-X|). Therefore, statement 1 is sufficient.
Pitfalls
The most typical pitfall is ignoring third step in opening modulus - always check whether your solution satisfies conditions.
Official GMAC Books:
The Official Guide, 12th Edition: PS #22; PS #50; PS #130; DS #1; DS #153;
The Official Guide, Quantitative 2th Edition: PS #152; PS #156; DS #96; DS #120;
The Official Guide, 11th Edition: DT #9; PS #20; PS #130; DS #3; DS #105; DS #128;
Generated from [GMAT ToolKit]
Resources
Absolute value DS problems: [search]
Absolute value PS problems: [search]
Fig's post with absolute value problems: [Absolute Value Problems]
For more information click here